Debugging #
Debugging WebRTC can be a daunting task. There are a lot of moving parts, and they all can break independently. If you aren’t careful, you can lose weeks of time looking at the wrong things. When you do finally find the part that is broken, you will need to learn a bit to understand why.
This chapter will get you in the mindset to debug WebRTC. It will show you how to break down the problem. After we know the problem, we will give a quick tour of the popular debugging tools.
Isolate The Problem #
When debugging, you need to isolate where the issue is coming from. Start from the beginning of the…
Signaling Failure #
Networking Failure #
Test your STUN server using netcat:
Prepare the 20-byte binding request packet:
echo -ne "\x00\x01\x00\x00\x21\x12\xA4\x42TESTTESTTEST" | hexdump -C 00000000 00 01 00 00 21 12 a4 42 54 45 53 54 54 45 53 54 |....!..BTESTTEST| 00000010 54 45 53 54 |TEST| 00000014Interpretation:
00 01is the message type.00 00is the length of the data section.21 12 a4 42is the magic cookie.- and
54 45 53 54 54 45 53 54 54 45 53 54(Decodes to ASCII:TESTTESTTEST) is the 12-byte transaction ID.
Send the request and wait for the 32 byte response:
stunserver=stun1.l.google.com;stunport=19302;listenport=20000;echo -ne "\x00\x01\x00\x00\x21\x12\xA4\x42TESTTESTTEST" | nc -u -p $listenport $stunserver $stunport -w 1 | hexdump -C 00000000 01 01 00 0c 21 12 a4 42 54 45 53 54 54 45 53 54 |....!..BTESTTEST| 00000010 54 45 53 54 00 20 00 08 00 01 6f 32 7f 36 de 89 |TEST. ....o2.6..| 00000020Interpretation:
01 01is the message type00 0cis the length of the data section which decodes to 12 in decimal21 12 a4 42is the magic cookie- and
54 45 53 54 54 45 53 54 54 45 53 54(Decodes to ASCII:TESTTESTTEST) is the 12-byte transaction ID. 00 20 00 08 00 01 6f 32 7f 36 de 89is the 12-byte data, interpretation:00 20is the type:XOR-MAPPED-ADDRESS00 08is the length of the value section which decodes to 8 in decimal00 01 6f 32 7f 36 de 89is the data value, interpretation:00 01is the address type (IPv4)6f 32is the XOR-mapped port7f 36 de 89is the XOR-mapped IP address
Decoding the XOR-mapped section is cumbersome, but we can trick the stun server to perform a dummy XOR-mapping, by supplying an (invalid) dummy magic cookie set to 00 00 00 00:
stunserver=stun1.l.google.com;stunport=19302;listenport=20000;echo -ne "\x00\x01\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00TESTTESTTEST" | nc -u -p $listenport $stunserver $stunport -w 1 | hexdump -C
00000000 01 01 00 0c 00 00 00 00 54 45 53 54 54 45 53 54 |........TESTTEST|
00000010 54 45 53 54 00 01 00 08 00 01 4e 20 5e 24 7a cb |TEST......N ^$z.|
00000020
XOR-ing against the dummy magic cookie is idempotent, so the port and address will be in clear in the response. This will not work in all situations, because some routers manipulate the passing packets, cheating on the IP address. If we look at the returned data value (last eight bytes):
00 01 4e 20 5e 24 7a cbis the data value, interpretation:00 01is the address type (IPv4)4e 20is the mapped port, which decodes to 20000 in decimal5e 24 7a cbis the IP address, which decodes to94.36.122.203in dotted-decimal notation.
Security Failure #
Media Failure #
Data Failure #
Tools of the trade #
netcat (nc) #
netcat is command-line networking utility for reading from and writing to network connections using TCP or UDP. It is typically available as the nc command.
tcpdump #
tcpdump is a command-line data-network packet analyzer.
Common commands:
Capture UDP packets to and from port 19302, print a hexdump of the packet content:
sudo tcpdump 'udp port 19302' -xxSame, but save packets in a PCAP (packet capture) file for later inspection:
sudo tcpdump 'udp port 19302' -w stun.pcapThe PCAP file can be opened with the Wireshark application:
wireshark stun.pcap
Wireshark #
Wireshark is a widely-used network protocol analyzer.
WebRTC browser tools #
Browsers come with built-in tools that you can use to inspect the connections you make. Chrome has chrome://webrtc-internals and chrome://webrtc-logs. Firefox has about:webrtc.
Latency #
How do you know you have high latency? You may have noticed that your video is lagging, but do you know precisely how much it is lagging? To be able to reduce this latency, you have to start by measuring it first.
True latency is supposed to be measured end-to-end. That means not just the latency of the network path between the sender and the receiver, but the combined latency of camera capture, frame encoding, transmission, receiving, decoding and displaying, as well as possible queueing between any of these steps.
End-to-end latency is not a simple sum of latencies of each component.
While you could theoretically measure the latency of the components of a live video transmission pipeline separately and then add them together, in practice, at least some components will be either inaccessible for instrumentation, or produce significantly different results when measured outside the pipeline. Variable queue depths between pipeline stages, network topology and camera exposure changes are just a few examples of components affecting end-to-end latency.
The intrinsic latency of each component in your live-streaming system can change and affect downstream components. Even the content of captured video affects latency. For example, many more bits are required for high frequency features such as tree branches, compared to a low frequency clear blue sky. A camera with auto exposure turned on may take much longer than the expected 33 milliseconds to capture a frame, even if when the capture rate is set to 30 frames per second. Transmission over the network, especially so cellular, is also very dynamic due to changing demand. More users introduce more chatter on the air. Your physical location (notorious low signal zones) and multiple other factors increase packet loss and latency. What happens when you send a packet to a network interface, say WiFi adapter or an LTE modem for delivery? If it can not be immediately delivered it is queued on the interface, the larger the queue the more latency such network interface introduces.
Manual end-to-end latency measurement #
When we talk about end-to-end latency, we mean the time between an event happening and it being observed, meaning video frames appearing on the screen.
EndToEndLatency = T(observe) - T(happen)
A naive approach is to record the time when an event happens and subtract it from the time at observation. However, as precision goes down to milliseconds time synchronization becomes an issue. Trying to synchronize clocks across distributed systems is mostly futile, even a small error in time sync produces unreliable latency measurement.
A simple workaround for clock sync issues is to use the same clock. Put sender and receiver in the same frame of reference.
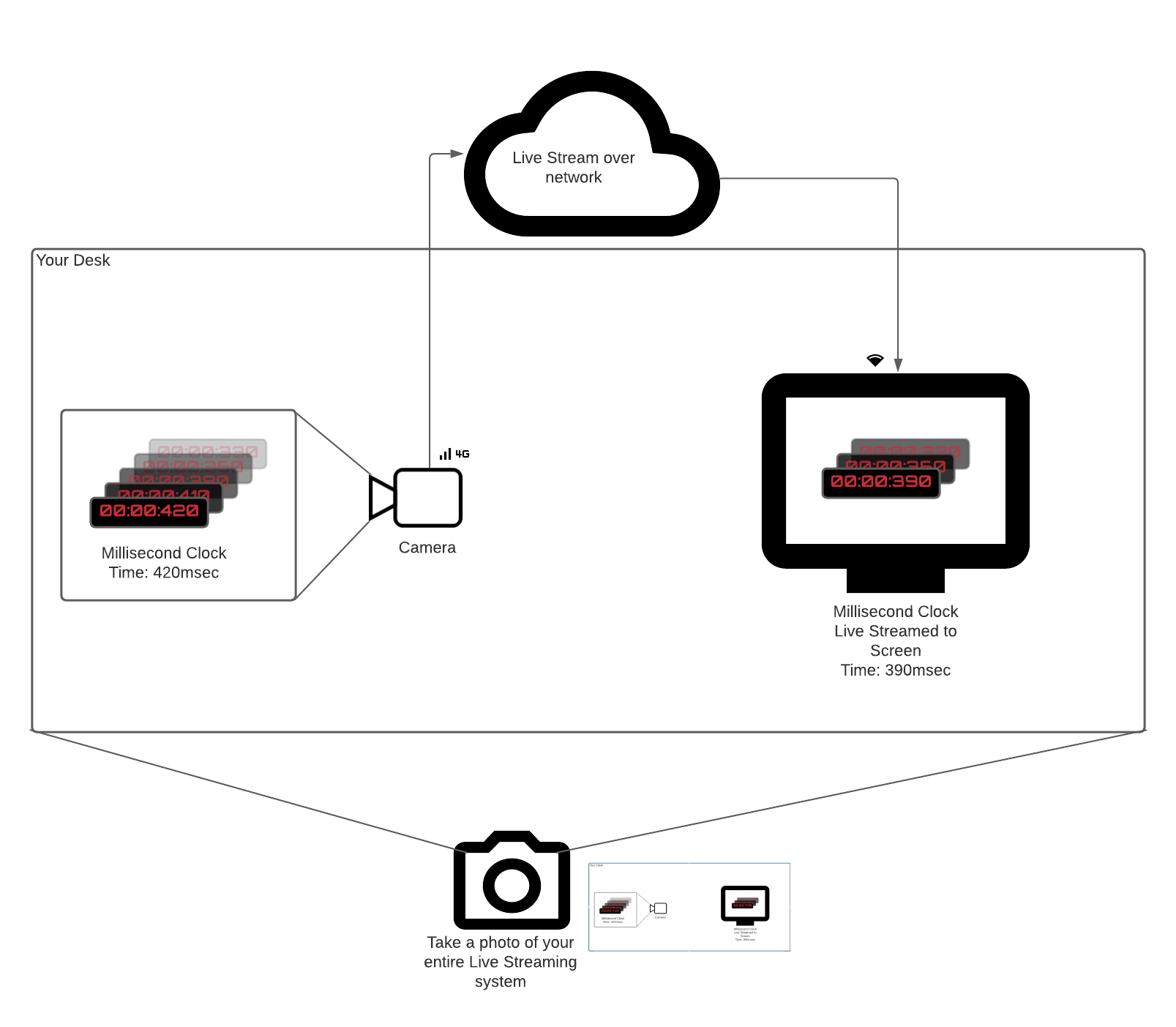
Imagine you have a ticking millisecond clock or any other event source really.
You want to measure latency in a system that live streams the clock to a remote screen by pointing a camera at it.
An obvious way to measure time between the millisecond timer ticking (Thappen) and video frames of the clock appear on screen (Tobserve) is the following:
- Point your camera at the millisecond clock.
- Send video frames to a receiver that is in the same physical location.
- Take a picture (use your phone) of the millisecond timer and the received video on screen.
- Subtract two times.
That is the most true-to-yourself end-to-end latency measurement. It accounts for all components latencies (camera, encoder, network, decoder) and does not rely on any clock synchronization.
 .
.
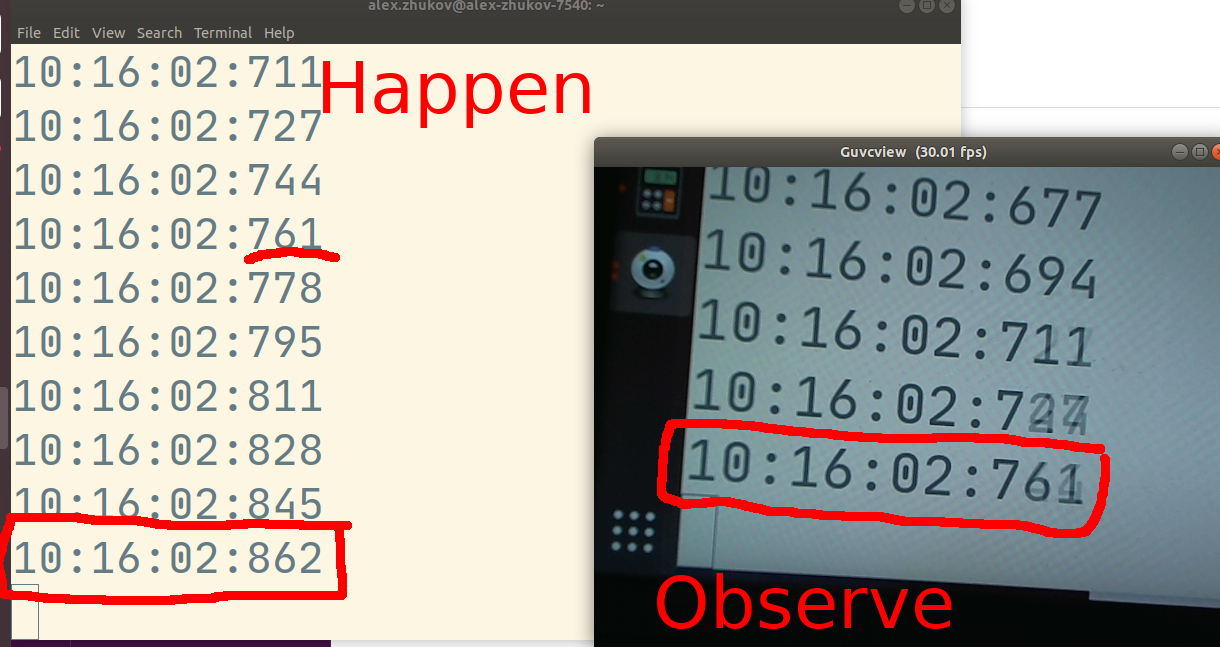 In the photo above measured end-to-end latency is 101 msec. Event happening right now is 10:16:02.862, but the live-streaming system observer sees 10:16:02.761.
In the photo above measured end-to-end latency is 101 msec. Event happening right now is 10:16:02.862, but the live-streaming system observer sees 10:16:02.761.
Automatic end-to-end latency measurement #
As of the time of writing (May 2021) the WebRTC standard for end-to-end delay is being actively discussed. Firefox implemented a set of APIs to let users create automatic latency measurement on top of standard WebRTC APIs. However in this paragraph, we discuss the most compatible way to automatically measure latency.
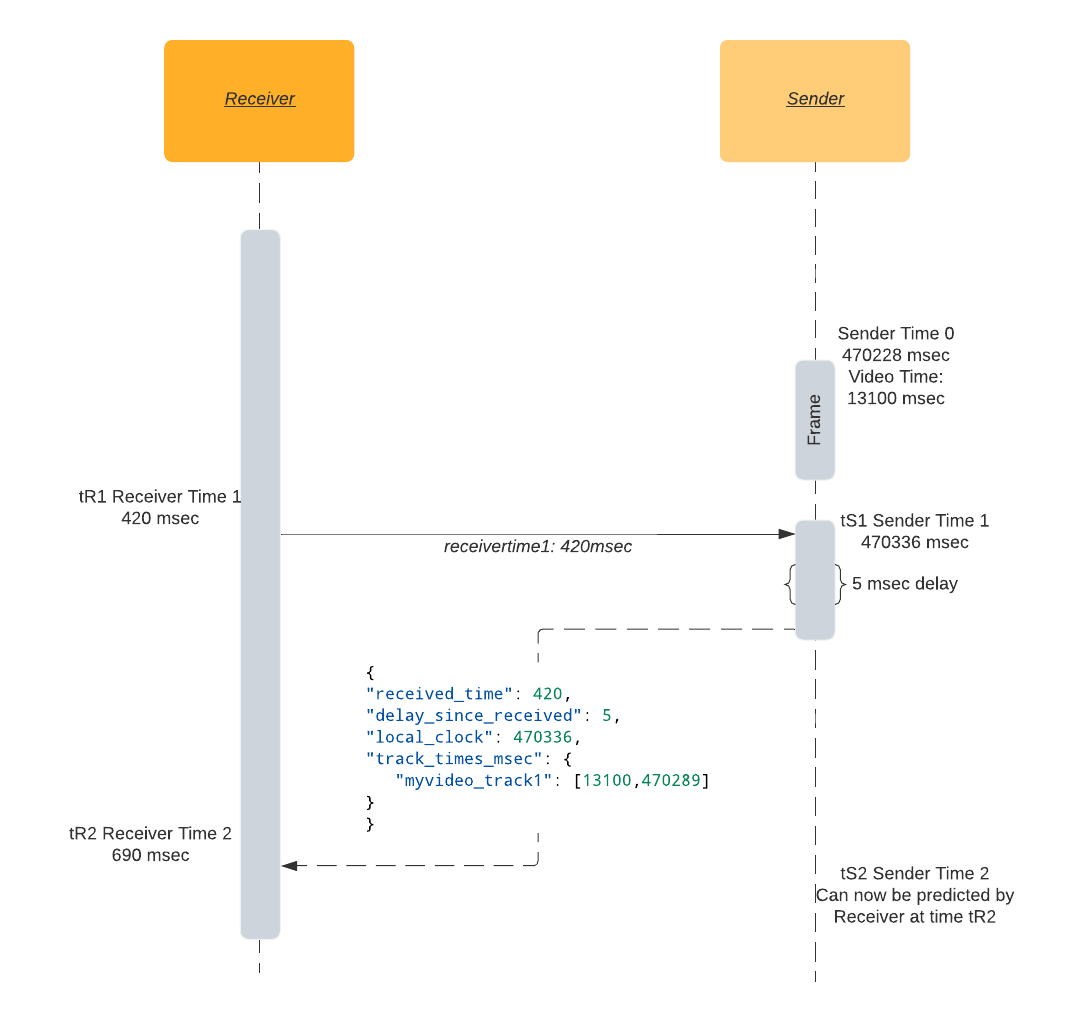
Roundtrip time in a nutshell: I send you my time tR1, when I receive back my tR1 at time tR2, I know round trip time is tR2 - tR1.
Given a communication channel between sender and receiver (e.g. DataChannel), the receiver may model the sender’s monotonic clock by following the steps below:
- At time
tR1, the receiver sends a message with its local monotonic clock timestamp. - When it is received at the sender with local time
tS1, the sender responds with a copy oftR1as well as the sender’stS1and the sender’s video track timetSV1. - At time
tR2on the receiving end, round trip time is calculated by subtracting the message’s send and receive times:RTT = tR2 - tR1. - Round trip time
RTTtogether with sender local timestamptS1is enough to create an estimation of the sender’s monotonic clock. Current time on the sender at timetR2would be equal totS1plus half of round trip time. - Sender’s local clock timestamp
tS1paired with video track timestamptSV1together with round trip timeRTTis therefore enough to sync receiver video track time to the sender video track.
Now that we know how much time has passed since the last known sender video frame time tSV1, we can approximate the latency by subtracting the currently displayed video frame’s time (actual_video_time) from the expected time:
expected_video_time = tSV1 + time_since(tSV1)
latency = expected_video_time - actual_video_time
This method’s drawback is that it does not include the camera’s intrinsic latency. Most video systems consider the frame capture timestamp to be the time when the frame from the camera is delivered to the main memory, which will be a few moments after the event being recorded actually happened.
Example latency estimation #
A sample implementation opens a latency data channel on the receiver and periodically sends the receiver’s monotonic timer timestamps to the sender. The sender responds back with a JSON message and the receiver calculates the latency based the message.
{
"received_time": 64714, // Timestamp sent by receiver, sender reflects the timestamp.
"delay_since_received": 46, // Time elapsed since last `received_time` received on sender.
"local_clock": 1597366470336, // The sender's current monotonic clock time.
"track_times_msec": {
"myvideo_track1": [
13100, // Video frame RTP timestamp (in milliseconds).
1597366470289 // Video frame monotonic clock timestamp.
]
}
}
Open the data channel on the receiver:
dataChannel = peerConnection.createDataChannel('latency');
Send the receiver’s time tR1 periodically. This example uses 2 seconds for no particular reason:
setInterval(() => {
let tR1 = Math.trunc(performance.now());
dataChannel.send("" + tR1);
}, 2000);
Handle incoming message from receiver on sender:
// Assuming event.data is a string like "1234567".
tR1 = event.data
now = Math.trunc(performance.now());
tSV1 = 42000; // Current frame RTP timestamp converted to millisecond timescale.
tS1 = 1597366470289; // Current frame monotonic clock timestamp.
msg = {
"received_time": tR1,
"delay_since_received": 0,
"local_clock": now,
"track_times_msec": {
"myvideo_track1": [tSV1, tS1]
}
}
dataChannel.send(JSON.stringify(msg));
Handle incoming message from the sender and print the estimated latency to the console:
let tR2 = performance.now();
let fromSender = JSON.parse(event.data);
let tR1 = fromSender['received_time'];
let delay = fromSender['delay_since_received']; // How much time that has passed between the sender receiving and sending the response.
let senderTimeFromResponse = fromSender['local_clock'];
let rtt = tR2 - delay - tR1;
let networkLatency = rtt / 2;
let senderTime = (senderTimeFromResponse + delay + networkLatency);
VIDEO.requestVideoFrameCallback((now, framemeta) => {
// Estimate current time of the sender.
let delaySinceVideoCallbackRequested = now - tR2;
senderTime += delaySinceVideoCallbackRequested;
let [tSV1, tS1] = Object.entries(fromSender['track_times_msec'])[0][1]
let timeSinceLastKnownFrame = senderTime - tS1;
let expectedVideoTimeMsec = tSV1 + timeSinceLastKnownFrame;
let actualVideoTimeMsec = Math.trunc(framemeta.rtpTimestamp / 90); // Convert RTP timebase (90000) to millisecond timebase.
let latency = expectedVideoTimeMsec - actualVideoTimeMsec;
console.log('latency', latency, 'msec');
});
Actual video time in browser #
<video>.requestVideoFrameCallback()allows web authors to be notified when a frame has been presented for composition.
Until very recently (May 2020), it was next to impossible to reliably get a timestamp of the currently displayed video frame in browsers. Workaround methods based on video.currentTime existed, but were not particularly precise.
Both the Chrome and Mozilla browser developers supported the introduction of a new W3C standard, HTMLVideoElement.requestVideoFrameCallback(), that adds an API callback to access the current video frame time.
While the addition sounds trivial, it has enabled multiple advanced media applications on the web that require audio and video synchronization.
Specifically for WebRTC, the callback will include the rtpTimestamp field, the RTP timestamp associated with the current video frame.
This should be present for WebRTC applications, but absent otherwise.
Latency Debugging Tips #
Since debugging is likely to affect the measured latency, the general rule is to simplify your setup to the smallest possible one that can still reproduce the issue. The more components you can remove, the easier it will be to figure out which component is causing the latency problem.
Camera latency #
Depending on camera settings camera latency may vary. Check auto exposure, auto focus and auto white balance settings. All the “auto” features of web cameras take some extra time to analyse the captured image before making it available to the WebRTC stack.
If you are on Linux, you can use the v4l2-ctl command line tool to control camera settings:
# Disable autofocus:
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 -c focus_auto=0
# Set focus to infinity:
v4l2-ctl -d /dev/video0 -c focus_absolute=0
You can also use the graphical UI tool guvcview to quickly check and tweak camera settings.
Encoder latency #
Most modern encoders will buffer some frames before outputting an encoded one. Their first priority is a balance between the quality of the produced picture and bitrate. Multipass encoding is an extreme example of an encoder’s disregard for output latency. During the first pass encoder ingests the entire video and only after that starts outputting frames.
However, with proper tuning people have achieved sub-frame latencies.
Make sure your encoder does not use excessive reference frames or rely on B-frames.
Every codec’s latency tuning settings are different, but for x264 we recommend using tune=zerolatency and profile=baseline for the lowest frame output latency.
Network latency #
Network latency is the one you can arguably do least about, other than upgrading to a better network connection. Network latency is very much like the weather - you can’t stop the rain, but you can check the forecast and take an umbrella. WebRTC is measuring network conditions with millisecond precision. Important metrics are:
- Round-trip time.
- Packet loss and packet retransmissions.
Round-Trip Time
The WebRTC stack has a built-in network round trip time (RTT) measurement mechanism.
A good-enough approximation of latency is half of the RTT. It assumes that it takes the same time to send and receive a packet, which is not always the case.
RTT sets the lower bound on the end-to-end latency.
Your video frames can not reach the receiver faster than RTT/2, no matter how optimized your camera to encoder pipeline is.
The built-in RTT mechanism is based on special RTCP packets called sender/receiver reports. Sender sends its time reading to receiver, the receiver in turn reflects the same timestamp to the sender. Thereby the sender knows how much time it took for the packet to travel to the receiver and return back. Refer to Sender/Receiver Reports chapter for more details of RTT measurement.
Packet loss and packet retransmissions
Both RTP and RTCP are protocols based on UDP, which does not have any guarantee of ordering, successful delivery, or non-duplication. All of the above can and does happen in real world WebRTC applications. An unsophisticated decoder implementation expects all packets of a frame to be delivered for the decoder to successfully reassemble the image. In presence of packet loss decoding artifacts may appear if packets of a P-frame are lost. If I-frame packets are lost then all of its dependent frames will either get heavy artifacts or won’t be decoded at all. Most likely this will make the video “freeze” for a moment.
To avoid (well, at least to try to avoid) video freezing or decoding artifacts, WebRTC uses negative acknowledgement messages (NACK). When the receiver does not get an expected RTP packet, it returns a NACK message to tell the sender to send the missing packet again. The receiver waits for the retransmission of the packet. Such retransmissions cause increased latency. The number of NACK packets sent and received is recorded in WebRTC’s built-in stats fields outbound stream nackCount and inbound stream nackCount.
You can see nice graphs of inbound and outbound nackCount on the webrtc internals page.
If you see the nackCount increasing, it means the network is experiencing high packet loss, and the WebRTC stack is doing its best to create a smooth video/audio experience despite that.
When packet loss is so high that the decoder is unable to produce an image, or subsequent dependent images like in the case of a fully lost I-frame, all future P-frames will not be decoded.
The receiver will try to mitigate that by sending a special Picture Loss Indication message (PLI).
Once the sender receives a PLI, it will produce a new I-frame to help the receiver’s decoder.
I-frames are normally larger in size than P-frames. This increases the number of packets that need to be transmitted.
Like with NACK messages, the receiver will need to wait for the new I-frame, introducing additional latency.
Watch for pliCount on the webrtc internals page. If it increases, tweak your encoder to produce less packets or enable a more error resilient mode.
Receiver side latency #
Latency will be affected by packets arriving out of order. If the bottom half of the image packet comes before the top you would have to wait for the top before decoding. This is explained in the Solving Jitter chapter in great detail.
You can also refer to the built-in jitterBufferDelay metric to see how long a frame was held in the receive buffer, waiting for all of its packets until it was released to the decoder.